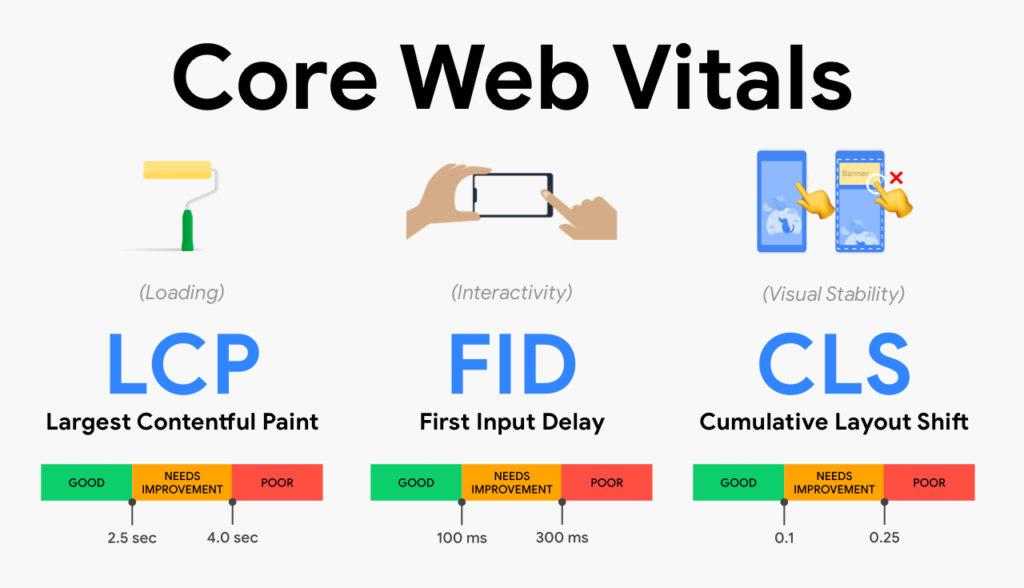
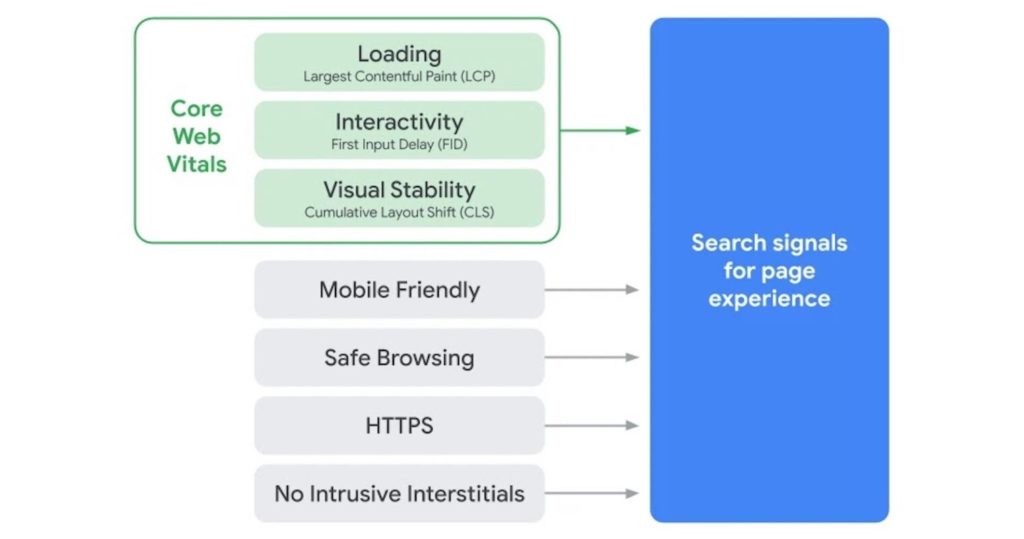
Core web vitals is a new website user experience criteria created by Google. The metrics track key elements such as loading, interactivity, and visual stability.
With the introduction of several new website usability and website user experience criteria designed by Google, many website owners are concerned with how they will assess their current site performance. Unfortunately, there is a huge amount of data available on the Internet, all of which may not be appropriate for certain purposes. In this article, we will discuss the most important metrics that should be used to evaluate a website’s performance.
The New Page Experience Signal to help website owners prepare for changes, Google has given an early glimpse at the work that is currently being done. The New Page Experience Signal includes the following core web usability metrics: Mobile-friendliness, site loading speed, site navigation, and site error messages.
These are just a few of the most critical core web usability metrics that are used by both website designers and developers. It is up to the designer or developer to match these new measurements with existing web usability and website user experience criteria and measurements.
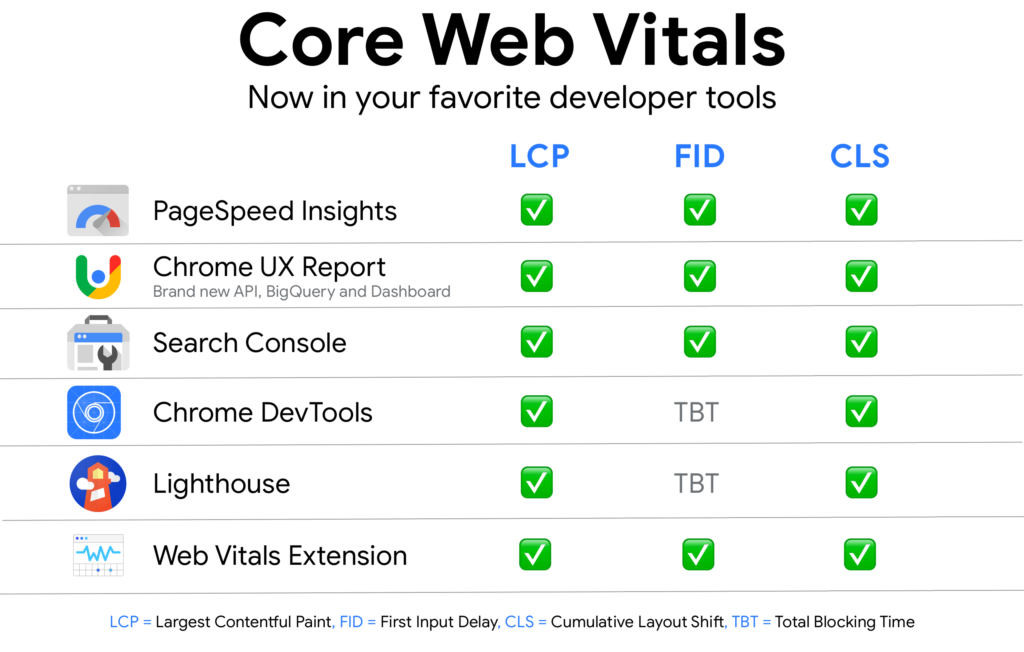
Site loading time is important because it is directly related to website usability, and many website owners are not satisfied with their site’s loading speed. Besides, most users will prefer a faster and more reliable web experience that uses fewer network resources. While the site loading time measurement is relatively easy, the selection of metrics is not as straightforward.
As previously mentioned, web page loading time is a measure of website usability. Although a website owner does not always control how quickly the pages load, he or she can control other aspects of the page, such as the content or graphics.
By controlling these aspects, a website owner can ensure that they provide good user experiences while providing adequate information to the website user. If a page cannot load, the user experience can be greatly affected and is likely to cause dissatisfaction.
A site owner must also measure site loading speed in order to measure user experience.
While a number of websites use JavaScript code to load pages, this does not guarantee that the pages load fast. A site’s ability to load depends on many factors, including the type of page, how it is written, and the amount of JavaScript code it uses.
There are a number of different web usability and website user experience criteria that can be applied to a website to determine its ability to load, such as:
Internet Explorer. For example, an Internet Explorer user will want a website to load fast because it is not compatible with many of its features. If a page takes longer to load than it is easy to navigate, an Internet Explorer user is likely to give up the website and move on to the next one.
Another aspect of web usability and website user experience that determines how fast the page loads is the presence or absence of error messages. Error-free sites can be considered more comfortable to use since users will be able to navigate the website without any issues. Some websites use HTML coding that is not correctly formatted, while others use complicated scripting languages.
One of the most important aspects of website usability and website user experience criteria is the ability of a site to provide information to the user. Although a site can be easily navigated with JavaScript or Flash code, it is essential to consider the types of pages that the user needs to access, and how quickly they are presented.
If a web page contains too much text, the user has trouble reading it or gets distracted by distracting elements, such as images and links. For this reason, users tend to become impatient when waiting for the page to load. A web page is also better off using images that have a consistent size and format.
Sites that do not load quickly should be redesigned in order to make the pages easier to read. Websites with poor navigation are often not used anymore because they do not offer enough information to the user, so there is usually no need to look at them.
Google Web Vitals – Conclusion
When a website fails to load, it is important to note its URL, which is often displayed on a separate web page, in addition to the actual title and information about the website. The URL should be kept short and precise, to prevent the user from being redirected to the incorrect page, which can cause additional problems for the user.

